IBM CAS Project: Improved Testing of VLSI Chips with Power Constraints
The elevated power dissipation during test has severe impact on test time, test reliability and product reliability, especially for high-performance processors like the Cell Processor. In the course of this project, new methods for test planning that take advantage of clock gating and power gating are developed.
10.2005 - 12.2009, IBM CAS-Project
Project Description
Built-in self test is a major part of the manufacturing test procedure for the Cell Processor. However, pseudo random patterns cause a high switching activity which is not effectively reduced by standard low power design techniques. If special care is not taken, the scan-speed may have to be reduced significantly, thus extending test time and costs.
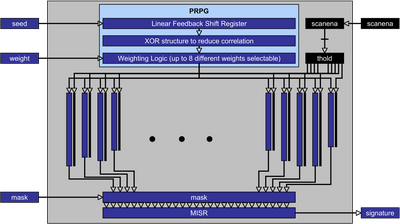
A test power reduction method for logic BIST is being developed which uses test scheduling, planning and scan-gating. In LBIST, effective patterns that detect additional faults are very scarce after a few dozens of scan cycles and often less than one pattern in a hundred detects new faults. In most cases, such an effective pattern requires only a reduced set of the available scan chains to detect the fault and all don't-care scan chains can be disabled, therefore significantly reducing test power.

Hans-Joachim Wunderlich
Prof. Dr. rer. nat. habil.Research Group Computer Architecture,
retired

